Learners : Matchbox recommender : Learner API : Data mappings
Negative data generation mapping
The Matchbox model is designed to operate on star ratings. That is, users are expected to explicitly rate items. However, in practice we often have to deal with the so-called “positive-only data” where users only indicate positive preferences to the items instead of explicitly rating them. Such data can be generated when users click on pages, buy products, play games, watch movies, etc.
In order to adapt such data to Matchbox we need to pre-process it by adding explicit negative ratings. One option is to consider all missing ratings as negatives. However, this will cause the training time to be proportional to the number of users times the number of items, while we want training time to be linear with the number of instances.
A common technique is to generate as many negatives as positives we have. By doing this, we still preserve the sparsity of the user-item matrix, while transforming the data in a format consumable by Matchbox. The negative data generation must be treated with care though, because we do not want to introduce any undesired biases. In order to achieve this, we need to generate as many negatives for each user as positives there are, and as many negatives for each item as there are positives. To illustrate this, consider the following training data:
u1, i1
u2, i1
u2, i3
u3, i2
u4, i4
It is easier to visualize the data this way:
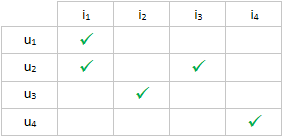
We want to sample the negatives in a way that the number of positives and negatives in each column and row is equal. That is, one example result looks like this:
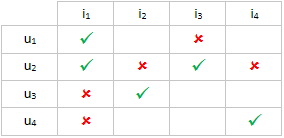
This procedure is implemented in the NegativeDataGeneratorMapping class. This mapping reads the training data through an implementation of the IRecommenderMappin interface. IRecommenderMapping declares methods which provide the users, items, and their features, but not the ratings (as there are no ratings in positive-only data). NegativeDataGeneratorMapping can be instantiated using the WithGeneratedNegativeData extension method on the IRecommenderMapping interface.
Here is an example of the creation procedure. We use the mapping chaining of a positive-only data mapping and a negative data generation mapping to create a recommender which can be trained directly on the positive-only dataset:
PositiveOnlyDataset positiveOnlyDataset; // ... populate this
FeatureSource featureSource; // ... populate this
var positiveOnlyMapping = new PositiveOnlyDataMapping();
var negativeDataGeneratorMapping = positiveOnlyMapping.WithGeneratedNegativeData();
var recommender = MatchboxRecommender.Create(negativeDataGeneratorMapping);
recommender.Train(this.positiveOnlyDataset, this.featureSource);
Here is a sample implementation of the positive-only data mapping and a definition of the dataset holder classes it operates on:
[Serializable]
private class PositiveOnlyDataMapping : IRecommenderMapping <PositiveOnlyDataset, Tuple<string, string>, string, string, FeatureSource, Vector>
{
public IEnumerable<Tuple<string, string>> GetInstances(PositiveOnlyDataset instanceSource)
{ return instanceSource.Instances; }
public string GetUser(PositiveOnlyDataset instanceSource, Tuple<string, string> instance)
{ return instance.Item1; }
public string GetItem(PositiveOnlyDataset instanceSource, Tuple<string, string> instance)
{ return instance.Item2; }
public Vector GetUserFeatures(FeatureSource featureSource, string user)
{ return featureSource.UserFeatures[user]; }
public Vector GetItemFeatures(FeatureSource featureSource, string item)
{ return featureSource.ItemFeatures[item]; }
}
private class PositiveOnlyDataset
{
public List<Tuple<string, string>> Instances { get; set; }
}
private class FeatureSource
{
public IDictionary<string, Vector> UserFeatures { get; set; }
public IDictionary<string, Vector> ItemFeatures { get; set; }
}
The negative data generation mapping generates a negative for each positive. So the output of the GetInstances method that is fed into the recommender looks like this, for example:
u1, i1, 1
u1, i3, 0
u2, i1, 1
u2, i2, 0
u2, i3, 1
u2, i4, 0
u3, i2, 1
u3, i1, 0
u4, i4, 1
u4, i1, 0
The overall complexity of the negative data generation algorithm is O(N log N) where N is the number of input instances. This is implemented by first constructing a histogram of the item popularity, and then sampling without replacement for each instance. The input pair (uK, iK) gives two outputs: (uK, iK, 1) and (uK, iL, 0) , where iL is sampled from a sum tree, which gives the logarithmic component in the complexity.
